TIBCO Scribe® Online Connector For HTTP
Use the TIBCO Scribe® Online Connector for HTTP to build your own HTTP requests. The flexibility of HTTP allows you to configure Uri, Verb, Query Parameters, Headers, and Content. Content can be hard-coded in a formula or configured with the TIBCO Scribe® Online Connector for Mapper.
Connector Specifications
| Supported | |
|---|---|
|
Agent Types |
|
| Connect on-premise | X |
| Connect cloud | X |
| Data Replication Apps | |
| Source | |
| Target | |
| On Schedule Apps | |
| Source | X |
| Target | X |
| On Event Apps | |
| Source | X |
| Target | X |
| Flows | |
| Integration | X |
| Request-Reply | X |
| Message | X |
This Connector is available from the TIBCO Cloud™ Integration Marketplace. See Marketplace Connectors for more information.
Supported Entities
The HTTP Connector supports the following entities. Click a linked entity name for additional information when using that entity in TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect. For a list of additional operations by entity see Special Operations.
Special Operations
| Entity | Operations |
|---|---|
|
-Wait For Message |
|
|
-Send |
|
|
-Add |
Operation Details
Query, Fetch, and Lookup Blocks display for this Connector but are not supported.
All operations require a URI. Do not include query parameters in the URI, use the Add Block instead.
Wait For Message
The Wait for Message Block only supports the HttpMessage entity. Other entities display in the Block but are not supported.
When sending an inbound message to the HTTP Connector from a third-party system, there are several possible responses that correlate to HTTP status codes, as follows:
- 202 - Accepted. Message successfully received. The flow starts processing and a MessageId Response Header is sent back.
- 400 - Bad Request, such as a malformed or wrong token.
- 403 - Forbidden, such as requestor IP address is not whitelisted.
- 404 - Not Found, such as missing parameter or incorrect path.
- 405 - Method not allowed, such as must use POST.
- 500 - Internal Server Error, catch all message.
Send
- Supported operations are based on the available GET, POST, PUT, and Request methods in the API. These methods are displayed as entities inside the Send Block.
- The foundation of the Send Block is the CreateWith Block, which is typically used with Hierarchical Data to add a single record or a parent record that contains one or more child records. In the case of hierarchical data, the Add Block is used to Add child records for the parent record in the CreateWith Block. See CreateWith Block and Add Block.
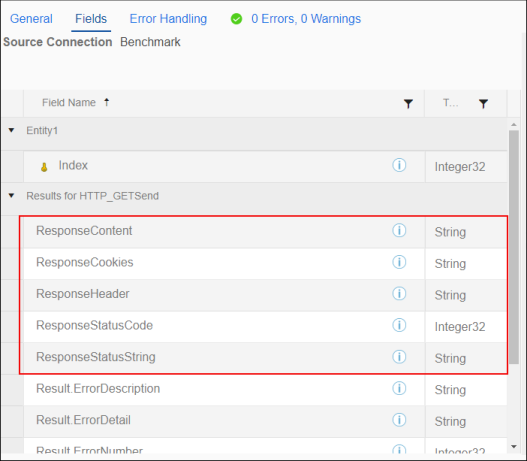
- When using the HTTP Connection as a target, Response fields displayed in the target side of the Send Block Fields tab are read-only.
Response field values returned by the API can be used as source data in subsequent Blocks.
Note: ResponseContent is returned as a string in the responding API's default format, such as JSON or XML. ResponseHeaders and ResponseCookies are serialized as JSON and are always returned as JSON. -
The HTTP requests where the content body is binary data, such as PDF files, are not supported.
Add
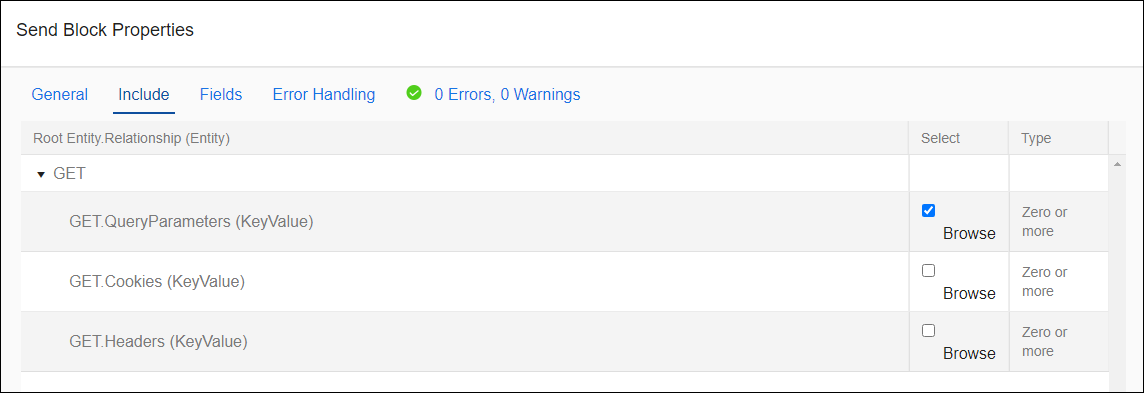
The Add Block works in conjunction with the Send Block, allowing you to add one or more Cookies, Headers, or QueryParameters to an HTTP request.
For this Connector, hierarchical relationships are used in http requests to include Cookies, Headers, and Query Parameters as children of the http method selected. Select Cookies, Headers, and Query Parameters on the Block Properties Include tab for the Send Block.
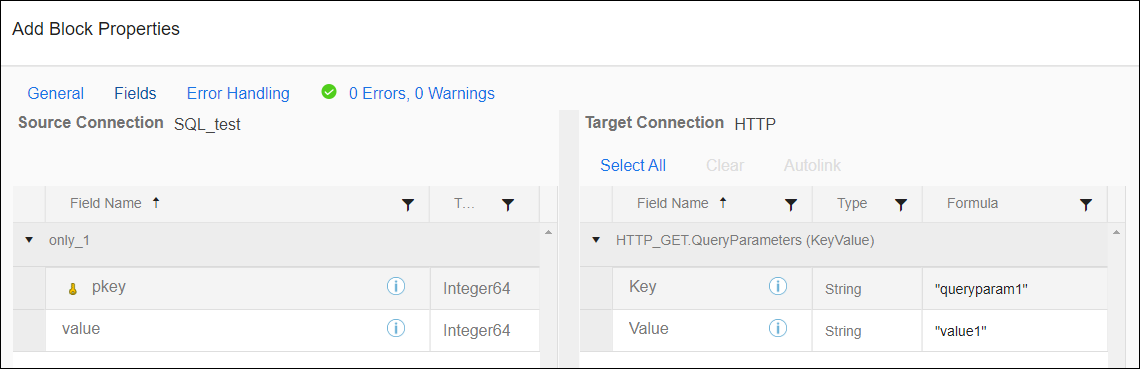
Child information is added using the Add Block Fields tab and is configured as key value pairs.
Setup Considerations
API Usage Limits
Some APIs limit the number of calls you can make. Refer to the documentation for the API you are accessing to determine what the limits are.
Selecting An Agent Type For HTTP
Refer to TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect Agents for information on available agent types and how to select the best agent for your app.
Connecting To HTTP
- Select Connections from the menu.
- From the Connections page select Create
 to open the Create a connection dialog.
to open the Create a connection dialog. - Select the Connector from
the list to open the Connection dialog, and then enter the following information for this Connection:
- Name — This can be any meaningful name, up to 25 characters.
- Alias — An alias for this Connection name. The alias is generated from the Connection name, and can be up to 25 characters. The Connection alias can include letters, numbers, and underscores. Spaces and special characters are not accepted. You can change the alias. For more information, see Connection Alias.
- Select Test to ensure that the agent can connect to your database. Be sure to test the Connection against all agents that use this Connection. See Testing Connections.
- Select OK/Save to save the Connection.
Notes On Entities
Special information about standard entities appears below.
Cookies
Used in an Add Block to add Cookies in the header when sending an HTTP request.
GET
- Configure this entity in a Send Block to request data from an API. GET returns JSON, XML, or other data from a web source.
- Use Query Parameters in an Add Block to filter response data for a GET method. When more than one Query Parameter is used, they are considered ANDs not ORs. For example if parameter1 is Country=US and parameter2 is State=NH, then both must be true for the data to be included in the response.
Headers
Used to create a dictionary of Headers using one or more Add Blocks configured with KeyValue pairs. For example, you could send authentication information.
HttpMessage
Used only in the Wait For Message Block in a Message or Request/ Reply flow to receive an inbound message from another system. Use the Send Block to POST or PUT the Contents of the message to a different API. The model of the inbound data is made available to subsequent Blocks in the Content field.
POST
Used to write data to a data source.
- Data is added to an existing record.
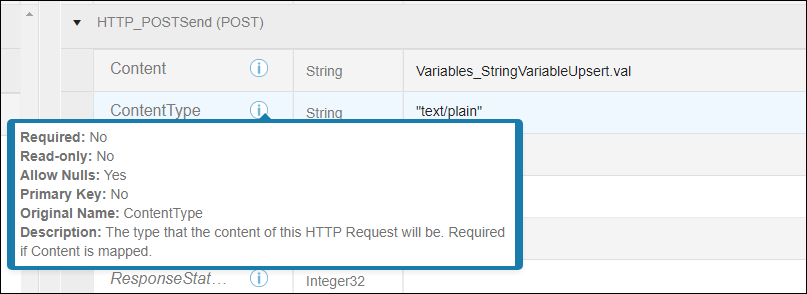
- ContentType —
- This field is required if the Content field is mapped.
- The Connector automatically appends charset_utf-8 to the ContentType field.
- Content length is calculated by the Connector.
PUT
Used to replace existing data.
- ContentType —
- This field is required if the Content field is mapped.
- The Connector automatically appends charset_utf-8 to the ContentType field.
- Content length is calculated by the Connector.
QueryParameters
Used to create a query string in an HTTP request. Use one or more Add Blocks configured with KeyValue pairs to add parameters. Do not enter ?, &, or other URL encoding. This is handled for you by the Connector. When more than one Query Parameter is used, they are considered ANDs not ORs.
Request
Used to support custom HTTP verbs. Select this entity in a Send Block and use the HttpVerb field on the Fields tab to configure one of the following:
- GET
- PUT
- POST
- PATCH
- DELETE
- OPTIONS
- TRACE
- HEAD
Sample Flows
In TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect, the REST Web Services Connector configures API calls for you based on a Swagger specification, but is limited to RESTful HTTP/API calls. You can use the HTTP Connector to configure customized HTTP/API calls.
These simple flows attempt to demonstrate some of these concepts and how they can be achieved using the HTTP Connector. Review the Group Block labels in the flows that explain the purpose of the Blocks inside the Group.
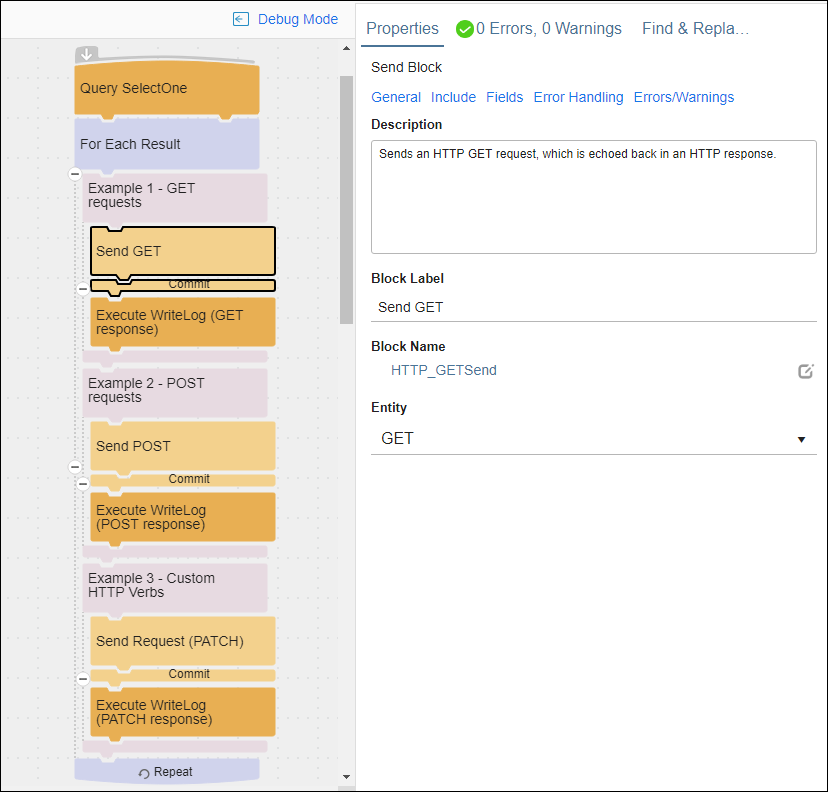
The Creating Requests by HTTP Verb flow demonstrates the following:
- Starting a flow with no source data for the Query Block.
- Using Send Blocks to send HTTP requests.
- Using Postman Echo to echo the entire HTTP request back to TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect.
- Recording that echoed response in the Agent log.
The Adding Request Details flow demonstrates the following:
- Adding query parameters by mapping the entire query in a formula field.
- Adding query parameters by selecting QueryParameters on the Include tab of the Send Block and using an Add Block for each parameter or Key Value pair.
- Adding headers by selecting Headers on the Include tab of the Send Block and using an Add Block for each header or Key Value pair.
- Adding cookies by selecting Cookies on the Include tab of the Send Block and using an Add Block for each cookie or Key Value pair.
- Using Postman Echo to echo each HTTP request back to TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect.
- Recording each echoed response in the Agent log.
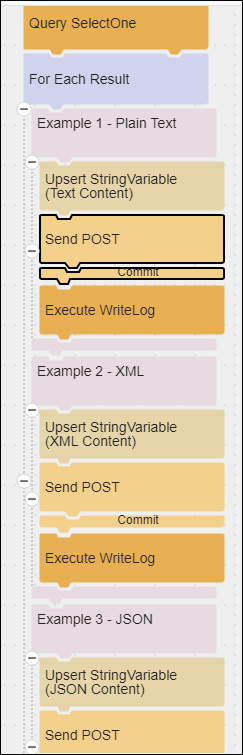
The Configuring Body with Content type flow provides examples for specific types of content and demonstrates the following:
- Using a string variable.
- Sending the value of the variable as content type plain text.
- Sending the value of the variable as content type XML.
- Sending the value of the variable as content type JSON.
- Using Postman Echo to echo each HTTP request back to TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect.
- Recording each echoed response in the Agent log.
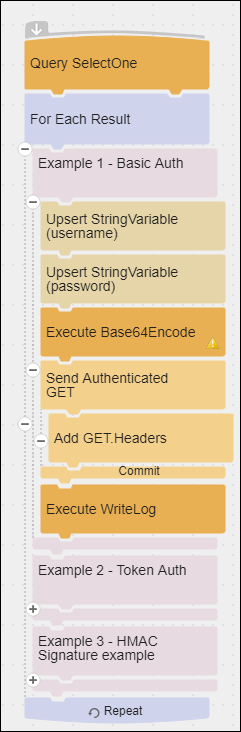
The Authenticating requests flow demonstrates how to configure authorization and authentication for HTTP web service calls, as follows:
- Using Basic Authentication.
- Store Username and Password as variables.
- Encode the Username and Password.
- Use a Send Block with Headers selected on the Include tab.
- Use an Add Block to send a header with a Key Value pair containing the authentication type and the encoded output.
- Using Token Authentication.
- Store ClientID and ClientSecret as variables.
- Use a Send Block to send the authentication information.
- Parse the token in the response to the Send Block. This step is not configured, but is represented by a Comment Block.
- Store the token as a variable.
- Use a Send Block with Headers selected on the Include tab.
- Use an Add Block to send a header with a Key Value pair containing the token variable.
- Using HMAC Signature.
- Store Access Key, HMAC Key, date stamp, and a string value as variables.
- Use an Execute Block to generate an HMAC256 Hash for a signature.
- Use a Send Block with Headers selected on the Include tab.
- Use an Add Block to send a header with a Key Value pair containing the authentication type and the encoded output.
- Using Postman Echo to echo each HTTP request back to TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect.
- Recording each echoed response in the Agent log.
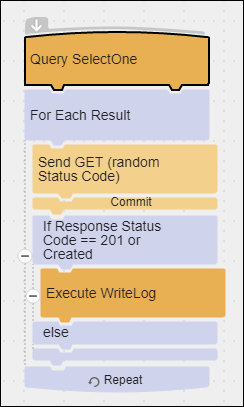
Some APIs may return more detailed status codes that can be used to modify flow behavior. For example, with an HTTP POST, a 201 code could indicate that the operation created a new record instead of updating an existing record. Review the documentation for the API you are accessing to determine if any of these codes would be useful to you. The Response Status Codes flow demonstrates the following:
- Sending a request that returns a status code. In this example the code returned is 201.
- Using an If/Else block to decide what to do if the status code returned is a 201 and what to do if it is any other code.
- Writing to the Agent log when a 201 status code is returned.
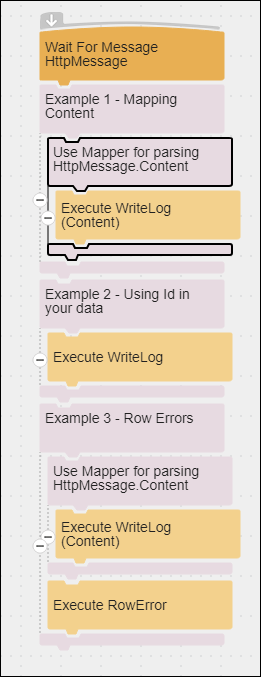
The HTTP Message Flow demonstrates the following:
- Support for Message flows
- Support for any string data, such as XML, JSON, or CSV.
- Responses to requests return a GUID (RequestID) that can be used in the flow.
TIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect API Considerations
To create connections with theTIBCO Cloud™ Integration - Connect API, the HTTP Connector requires the following information:
|
Connector Name |
HTTP |
|
Connector ID |
FB971315-E707-4869-88FA-9A14A5F42AA1 |
License Agreement
The TIBCO End User License Agreement for the HTTP Connector describes TIBCO and your legal obligations and requirements. TIBCO suggests that you read the End User License Agreement.
More Information
For additional information on this Connector, refer to the Knowledge Base and Discussions in the TIBCO Community.