TIBCO Scribe® Online Connector For Tools
The TIBCO Scribe® Online Connector For Tools provides special operations used as entities in the Query, Fetch, and Execute Blocks in your TIBCO Scribe® Online Maps to enhance the performance of the Map, functions, or provide diagnostic information.
Connector Specifications
| Supported | |
|---|---|
| Agent Types | |
| On Premises | X |
| Cloud | X |
| Replication Services | |
| Source | |
| Target | |
| Integration Services | |
| Source | X |
| Target | X |
| Migration Services | |
| Source | X |
| Target | X |
| Maps | |
| Integration | X |
| Request-Reply | X |
| Message | X |
This Connector is available from the TIBCO Scribe® Online Marketplace. See Marketplace TIBCO Scribe® Certified Connectors for more information.
Supported Entities
The Tools Connector supports the following entities. Click a linked entity name for additional information when using that entity in TIBCO Scribe® Online. For a list of additional operations by entity, see Special Operations.
Special Operations
| Entity | Operations |
|---|---|
|
-Query -Fetch -Lookup |
|
|
-Execute |
Selecting An Agent Type For Tools
Refer to TIBCO Scribe® Online Agents for information on available Agent types and how to select the best Agent for your Solution.
This Connector supports both the Cloud Service and the On-Premise Agent for the supported Solution types listed in the Connector Specifications table, regardless of the location of the data. Data can be in the cloud or on-premises. See Installing A TIBCO Scribe® Online On-Premise Agent or Provisioning A TIBCO Scribe® Online Cloud Service.
Note: If you use a Cloud Service with an on-premise datastore, you may need to whitelist the IP addresses of the Cloud Service managers to allow the Cloud Service to access your network. See Whitelisting Requirements.
Connecting to Tools
- Select More > Connections from the menu.
- From the Connections page, select Add
 to open the Add a New Connection dialog.
to open the Add a New Connection dialog. - Select the Connector from
the dropdown list in the Connection Type field, and then enter the following information for this Connection:
- Name — This can be any meaningful name, up to 25 characters.
- Alias — An alias for this Connection name. The alias is generated from the Connection name, and can be up to 25 characters. The Connection alias can include letters, numbers, and underscores. Spaces and special characters are not accepted. You can change the alias. For more information, see Connection Alias.
- Select Test to ensure that the Agent can connect to your database. Be sure to test the Connection against all Agents that use this Connection. See Testing Connections.
- Select OK/Save to save the Connection.
Tools Connector as IS Source
Consider the following when using the Tools Connector as an Integration Solution source.
- Net Change is not supported.
Notes on Entities and Operations
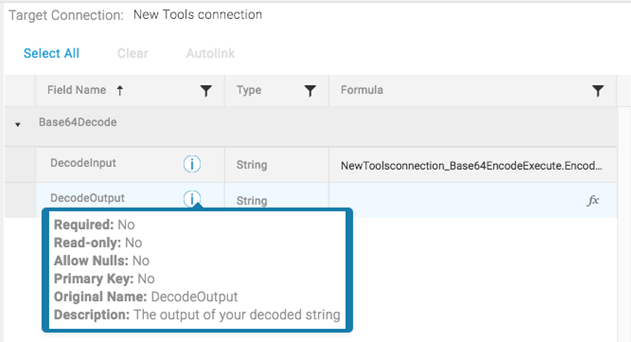
Base64Decode
Converts a Base64-encoded String to an un-encoded String.
- Base64Decode has one input property, DecodeInput.
- A NULL or empty DecodeInput value skips the block completely.
- An invalid DecodeInput value results in the record error.
DecodeOutput is an output property, used to convert your input base64 encoded string to its String value. This function works similar to the decode tool at the BASE64 Decode and Encode site. A common use-case is to validate base64 encoded values.
Base64DecodeToBytes
Converts a string to Bytes.
- Base64DecodeToBytes has one input property, DecodeInput.
- A NULL or empty DecodeInput value skips the Block completely.
- An invalid DecodeInput value results in a record error.

Base64EncodeToBytes
Converts Bytes to a string.
- Base64EncodeToBytes has one input property, EncodeInput.
- A NULL or empty EncodeInput value skips the Block completely.
- An invalid EncodeInput value results in a record error.

Base64Encode
Converts a String to Base64, ISO-8859-1 encoded string.
- Base64Encode has one input property, EncodeInput.
- A NULL or empty EncodeInput value skips the Block completely.
- An invalid EncodeInput value results in a record error.
EncodeOutput is an output property used to convert your input string to a base64 encoded value. This function works similar to the encode tool at the BASE64 Decode and Encode site. Common use-cases with this function might be to send a username and password, or clientId and clientSecret in an HTTP header - also known as Basic Authentication. Refer to the Basic access authentication page on Wikipedia for more information.

Dates
Converts a DateTime to other formats.
- The Dates entity has one input property, InputDate.
- A NULL or empty InputDate value skips the Block completely.
- An invalid InputDate value results in a record error.
Unix is an output property, used to convert your DateTime value into a Unix value, also known as POSIX or UNIX Epoch time. The function works in a way that is similar to the following tool: Epoch Converter. A common use-case for this function is to send an HTTP date header or append to a file name.

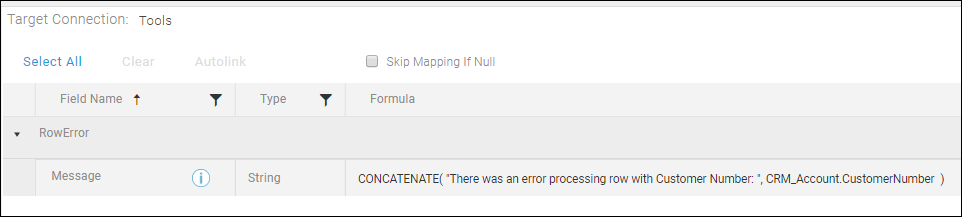
FatalError
Supports adding a custom message with a dynamic value to the error details when a Fatal Error occurs. Use this option to include data from the Map in your error message for better troubleshooting. For example, you might choose to include an account number to help locate a source record that is generating an error. This message is not affected by the settings on the Block Properties Error Handling tab.

Hash Functions
Supports the following functions:
- SHA1
- SHA256
- SHA384
- SHA512
These functions are cryptographic hash functions that take an input and produce a (string) hash value as the output.
- Each function has one input property, InputString.
- A NULL or empty InputString value skips the block completely.
OutputHash is an output property used to convert your input to the selected encoded Hash value. These functions work similar to the hash function online generator at http://www.sha1-online.com/. This is a one-way hash encoding process, there is no decoding. Common use-cases include hashing for pseudonymisation in GDPR and comparing hashed passwords, such as incoming Request/Reply and Message Maps with Hashed passwords, and known passwords stored in TIBCO Scribe® Online Maps/Lookup Tabs.

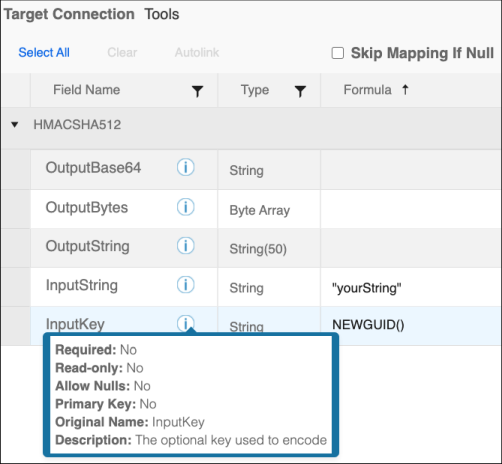
HMAC
HMAC is supported by using the SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, and SHA512 hash functions.
- Each function has one input property, InputString, with an optional key, InputKey.
- A NULL or empty InputString value skips the block completely.
- Output types include: Byte Array, String(50), and Base64Encoded String.
OutputBase64, OutputBytes, and OutputString are output properties used to convert your input to the selected encoded Hash value. A common use case is for creating API/Web Service authorization signatures.
RowError
Supports adding a custom message with a dynamic value to the error details when a record error occurs. Use this option to include data from the Map in your error message for better troubleshooting. For example, you might choose to include an account number to help locate a source record that is generating an error. To generate this error message, error handling must be enabled on the Error Handling tab of the Execute Block. If error handling is disabled, the custom message is not generated. If error handling is enabled, both the message on the Error Handling tab and the custom message are generated and are included in the Execution History Error Details.
SelectOne
- This entity is supported for the Query, Fetch, and Lookup Blocks.
- When used in a Query Block:
- Provides the ability to start a Map without querying a data source.
- Always returns the current time in UTC.
- Filters are not supported.

You can use the SelectOne entity to start a Map without running a query in cases where you would really prefer to use a Fetch Block to gather data. For example, your Map might use SelectOne in a Query to start, then use a REST Connector CreateWith Block and then a Fetch Block to provide data for an Add Block to build a hierarchical record.

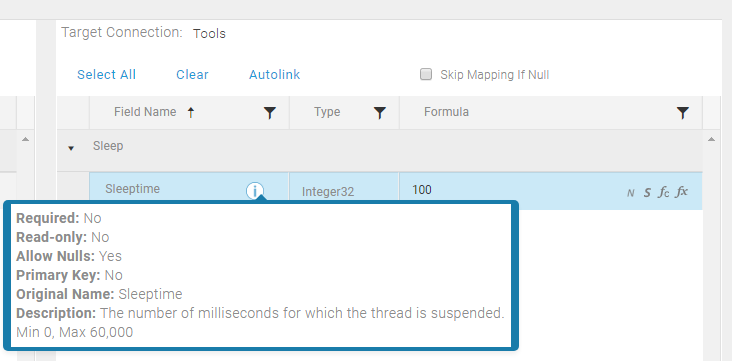
Sleep
Use the Sleep entity in an Execute Block to add a delay in a Map.
- Sleep has one property, SleepTime, which suspends the current thread for the specified number of milliseconds.
- Internally the SleepTime parameter is millisecondsTimeout.
- SleepTime must range from 0 to 60,000 ms.
- A NULL or empty SleepTime value skips the Block completely. An invalid SleepTime value results in record errors.
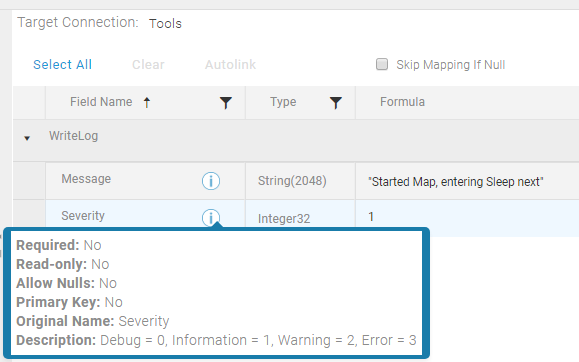
WriteLog
Use WriteLog in an Execute Block to add an entry into the Agent Log when the Block is encountered in the Map. WriteLog allows you to configure the log level where you want to add the entry. For example, to only log when the Agent is set to Warning, the Severity should be set to 2. You can add additional detail to the Agent log entry up to 2048 characters using the Message field.
Note: Requires that Debug be enabled on the Agent. See Editing Agent Settings for instructions on enabling Debug.
The Agent log includes messages similar to the following:

JsonToXml
The JsonToXml entity converts JSON data to XML format.
- JsonToXml has the JsonInput input property to insert the JSON data as a string.
- JsonToXml has the XmlOutput output property, which is the result of the conversion.
- If the JsonInput value is either NULL or empty, the value is returned as is.
- If the JsonInput value is invalid and cannot be converted to XML, a record error occurs.
- When you insert a JSON string directly into the Formula Editor, ensure that the text is according to the guidelines. For more information about the guidelines, see the Formula Editor help.
- You can also use the Files Connector to convert the JSON data on a file into a string when working on-premises, or use any method that inserts the JSON data into a string field.
Note: The differences between JSON and XML make complete conversion complex. The JsonToXml entity can be used for simple conversions only.
JSON to XML Conversion Rules
The JSON to XML conversion process follows specific rules to ensure a valid and consistent XML output.
Element Naming
-
XML element names allow only letters (either
atozorAtoZ), digits (0to9), underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.). -
The entity removes invalid characters from element names.
-
If a name does not start with a letter or underscore, an underscore is prepended.
-
If a name is empty, an underscore is prefixed.
Type Conversion
-
Objects: Each JSON object is converted into an XML element, with properties as child elements.
-
Arrays: Each array is converted to an XML element containing child elements named
Item(this name is configurable). -
Strings: Strings are converted directly to XML element text content.
-
Numbers:
-
Preserved as int32 when possible
-
Preserved as int64 for larger integers
-
Converted to decimal for floating-point numbers
-
-
Booleans: Booleans are converted to XML element text with values either
trueorfalse. -
Null Values: Null values are represented as an empty strings in XML.
Structure
-
Root Element: The entity wraps the JSON content in a configurable root element (default is
Root). -
Array Items: All array items use a consistent element name (default is
Item).
Not Currently Implemented
-
XML attributes (all JSON properties become elements)
-
Date parsing or special handling (check comments in the code)
-
XML namespace support
-
Advanced formatting options
XmlToJson
The XmlToJson entity converts XML data to JSON format.
- XmlToJson has the XmlInput input property to insert the XML data as a string.
- XmlToJson has the JsonOutput output property, which is the result of the conversion.
- If the XmlInput value is either NULL or empty, the value is returned as is.
- If the XmlInput value is invalid and cannot be converted to JSON, a record error occurs.
- When you insert an XML string directly into the Formula Editor, ensure that the text is according to the guidelines. For more information about the guidelines, see the Formula Editor help.
- You can also use the Files Connector to convert the XML data on a file into a string when working on-premises, or use any method that inserts the XML data into a string field.
XML to JSON Conversion Rules
The XML to JSON conversion process follows specific rules to ensure accurate and consistent data transformation.
Structure Conversion
-
Elements to Objects: Each XML element is converted to a JSON object.
-
Hierarchy Preservation: The parent-child structure of XML elements is maintained as nested JSON objects.
Property Handling
-
Attributes: XML attributes become direct properties of the JSON object, using the attribute names as keys.
-
Child Elements: Each child element becomes a property of the parent object, with the element name as the property key and the converted value as the property value.
Value Handling
-
Element Values: If an element has no child elements but contains text content, the content is stored as a
valueproperty in the JSON object. -
Empty Elements: Elements with no text content and no children become empty JSON objects.
Xslt
The Xslt entity transforms XML data using an XSLT style sheet.
- Xslt has the following input properties:
- The XmlInput property can be used to insert XML data as a string.
- The XsltInput property can be used to insert XSLT data as a string.
- Xslt has the Output output property, which is the result of the transformation.
- If either XmlInput or XsltInput value is invalid, a record error occurs.
- When you insert an XML or XSLT string directly into the Formula Editor, ensure that the text is according to the guidelines. For more information about the guidelines, see the Formula Editor help.
- You can also use the Files Connector to convert the XML or XSLT data on a file into a string when working on-premises, or use any method that inserts the XML or XSLT data into a string field.
XML and XSLT Transformation Example
The following is an example of XML and XSLT transformation:
If the XmlInput is:
<string>
<message> Hello, World!</message>
</string>
And the XsltInput is:
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<body>
<h2>Message</h2>
<p><xsl:value-of select="string/message"/></p>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Then the Output comes out as:
<html>
<body>
<h2>Message</h2>
<p> Hello, World!</p>
</body>
</html>
Sample Maps
Note: To download the Sample Maps, go to the Tools Sample Maps Knowledge Base article in the TIBCO Community.
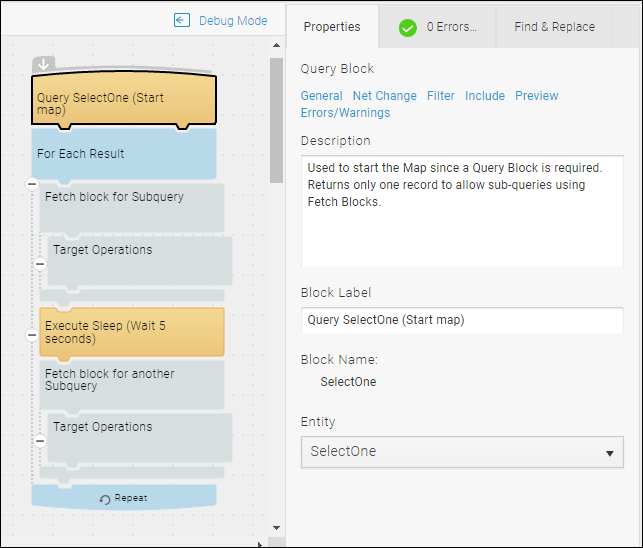
In TIBCO Scribe® Online, there is no mechanism for encoding and decoding information, adding custom messages to the Agent log, or pausing a Map. In addition, the requirement of a Query Block can be limiting depending on what you are trying to accomplish. Using the Query Block with the Tools SelectOne entity only returns one record with a datetime. By using the SelectOne entity to start the Map, you can use Fetch Blocks to create sub-queries. For example, if you wanted to integrate Accounts and Customers into a Microsoft SQL Server database, you can do that within two Fetch Blocks. You can use these Maps to learn about Debug also.
These simple Maps attempt to demonstrate some of these concepts and how they can be achieved using the Tools Connector. Review the Block descriptions in the Maps that explain the purpose of the associated Block.
You can change the way the maps process - Map demonstrates the following:
- Starting a Map with no source data for the Query Block.
- Using Fetch Blocks to return and process different sets of data.
- Executing a Sleep timer to pause the Map.
The Adding custom logging and errors Map demonstrates the following:
- Mapping dynamic values to the Agent logs.
- Mapping a dynamic value as a Fatal Error message.
- Mapping a dynamic value as a Record Error message.
The following errors are not real and are just for demonstrating error logging.

The Encoding and converting values Map demonstrates the following:
- Converting a DateTime to UNIX/Epoch.
- Encoding a value to Base64.
- Decoding a Base64 value.
- Encoding a value to SHA1.

The Converting String <-> Byte Array Map demonstrates the following:
- Creating a variable for storing a CSV object and populating it.
- Converting a string to a byte array.
- Converting a byte array to a string.

TIBCO Scribe® Online API Considerations
To create connections with the TIBCO Scribe® Online, the Tools Connector requires the following information.
|
Connector Name |
Tools |
|
Connector ID |
EB930ED7-CFDB-479F-8EFB-70BDB4AC6EA8 |
License Agreement
The TIBCO Scribe® Online End User License Agreement for the Tools Connector describes TIBCO and your legal obligations and requirements. TIBCO suggests that you read the End User License Agreement.
More Information
For additional information on this Connector, refer to the Knowledge Base and Discussions in the TIBCO Community.

